This thread documents the progress of planning, execution, and analysis of an Experiment conducted by Sandor Szekely (a believer in the "Flat Earth" theory) on Lake Balaton in Hungary. The goal of the experiment was to measure the curvature of the surface of a lake by shining a laser across it, and measuring the height of the laser at multiple points across the lake. If the lake was curved then plotting those heights on a graph should form a curve. If it was flat, then it would form a straight line.
The experiment was extensively documented with photos and video.
The results of the experiment were some very poor quality data. Poor initial calibration of the laser mean that the it was pointing slightly downwards instead of the intended level or slightly upwards. The laser target used was positioned so that the laser very quickly rose above it and could no longer be measured, and the laser beam diverged rapidly so as to be impossible to locate.
Since the laser seems to have been pointing downwards, the subsequent rise of the laser above the target is most consistent with a curved surface. However the very poor quality of the measurements makes this impossible to quantify.
Here re some pre-experiment key posts that were discussed:
Since the laser cannot be leveled exactly, multiple readings should be taken to calculate both the curve of the lake and the slope of the laser
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...vature-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/#post-186843
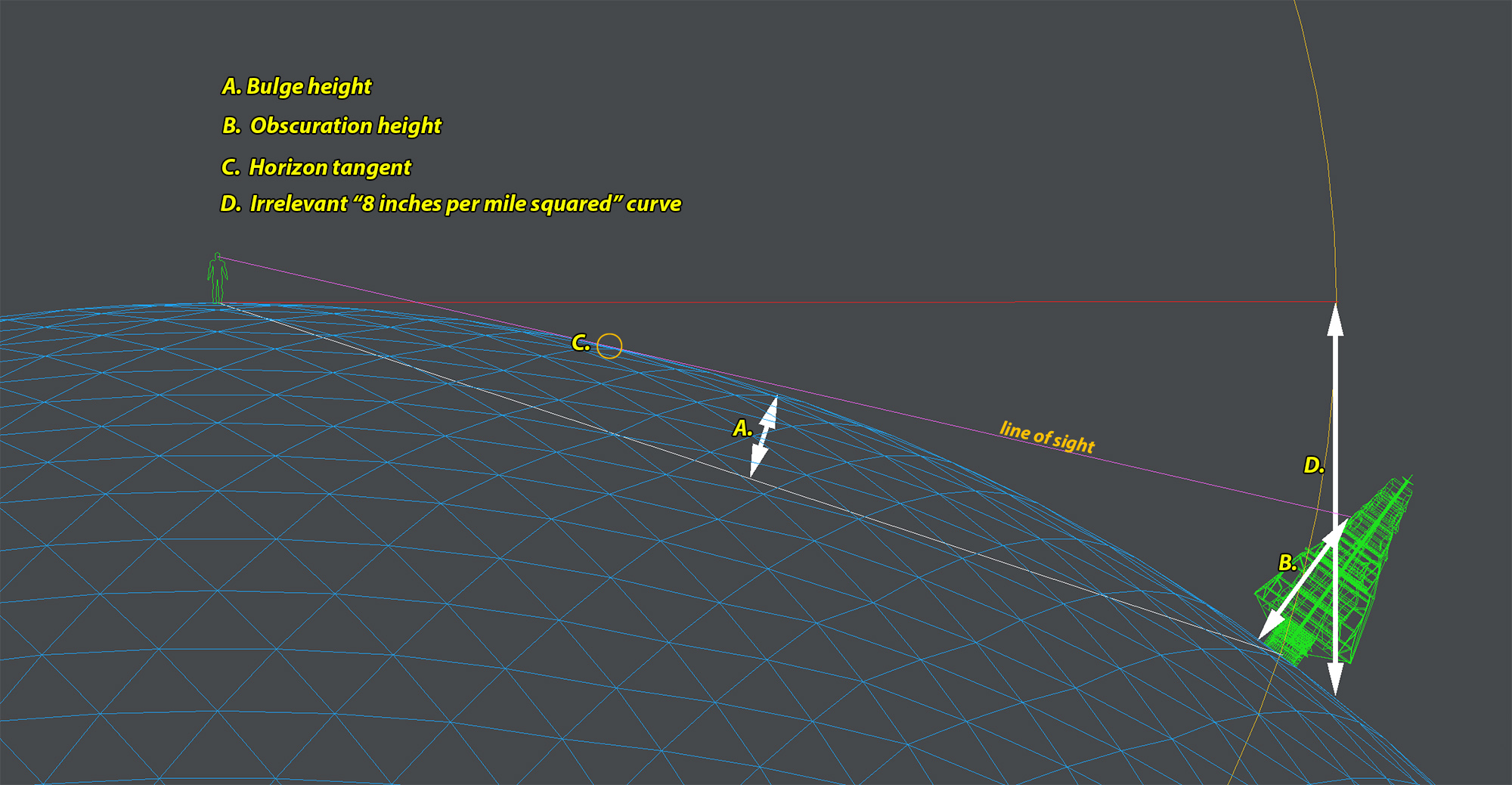
If the laser is pointing down a bit, then it will initially match the curve of the earth, and so appear to be level for the first mile or two.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-2#post-186880
A much more accurate "Wallace" method was suggested several times:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-3#post-187601
Initial results from the experiment started to be discussed here:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-4#post-188309
The experiment at night was unusable due to refraction of the beam, but gave some excellent photos of this refraction and inferior mirage. This led to some interesting discussion.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-4#post-188365
The refraction was due to the water temperature being warmer than the air temperature
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-5#post-188421
The discussion of the results published on YouTube starts here:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-13#post-190061
The following is a list of posts that identify issues with the experiment.
Calibration of the laser height was done with a tape measure at an angle of 20° from vertical, leading to it being lower than intended.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190631
Using the 1m edge of the board as a guide the height of the target tape is measured at under 1.20m, but was claimed to be 1.30m. Since the laser itself was at 1.25m, this means the laser was pointing downwards.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190631
Some measurements were taken with the boat stationary, some with it underway, resulting in an approximately 5cm variation.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190668
Times on the photo comparisons do not match, being several minutes off in some cases:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-16#post-190262
After the laser left the target, subsequent sightings were only from a retroreflective patch on the back of the pilot's jacket, and from reflections off the camera glass.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190576
The motion of these reflections through the beam indicate that it eventually diverged to several feet wide, from the camera glass reflection
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190574
And from the earlier jacket retroreflective patch
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190623
Some later measurements were claimed to be from a "direct hit" in a camera on the boat, however these "direct hits" lasted for over a minute while the boat moved significant distances perpendicular to the beam. This indicated a "direct hit" could be had anywhere within a large cone, meaning height estimates were possibly catching the bottom of the cone.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190419
It was suggested geoid variations might be a factor, but did not seem to be significant
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-14#post-190169
Sandor claimed that a LIDAR study of the lake found it was flat, and that he had got confirmation of this. The lead author of the study refuted this.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-23#post-190877
Sandor started a thread on scienceforums.net, and his OP seemed to suggest he was part of the LIDAR study, when he was not.
http://www.scienceforums.net/topic/98386-laser-curvature-test-on-lake-balaton/
Sandor was banned for a cumulation of violations of the posting guidelines, ending with his blatant misrepresentation of this paper (which actually proved the lake surface was curved exactly as would be expected)
The experiment was extensively documented with photos and video.
The results of the experiment were some very poor quality data. Poor initial calibration of the laser mean that the it was pointing slightly downwards instead of the intended level or slightly upwards. The laser target used was positioned so that the laser very quickly rose above it and could no longer be measured, and the laser beam diverged rapidly so as to be impossible to locate.
Since the laser seems to have been pointing downwards, the subsequent rise of the laser above the target is most consistent with a curved surface. However the very poor quality of the measurements makes this impossible to quantify.
Here re some pre-experiment key posts that were discussed:
Since the laser cannot be leveled exactly, multiple readings should be taken to calculate both the curve of the lake and the slope of the laser
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...vature-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/#post-186843
If the laser is pointing down a bit, then it will initially match the curve of the earth, and so appear to be level for the first mile or two.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-2#post-186880
A much more accurate "Wallace" method was suggested several times:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-3#post-187601
Initial results from the experiment started to be discussed here:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-4#post-188309
The experiment at night was unusable due to refraction of the beam, but gave some excellent photos of this refraction and inferior mirage. This led to some interesting discussion.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-4#post-188365
The refraction was due to the water temperature being warmer than the air temperature
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...-of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-5#post-188421
The discussion of the results published on YouTube starts here:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-13#post-190061
The following is a list of posts that identify issues with the experiment.
Calibration of the laser height was done with a tape measure at an angle of 20° from vertical, leading to it being lower than intended.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190631
Using the 1m edge of the board as a guide the height of the target tape is measured at under 1.20m, but was claimed to be 1.30m. Since the laser itself was at 1.25m, this means the laser was pointing downwards.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190631
Some measurements were taken with the boat stationary, some with it underway, resulting in an approximately 5cm variation.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190668
Times on the photo comparisons do not match, being several minutes off in some cases:
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-16#post-190262
After the laser left the target, subsequent sightings were only from a retroreflective patch on the back of the pilot's jacket, and from reflections off the camera glass.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190576
The motion of these reflections through the beam indicate that it eventually diverged to several feet wide, from the camera glass reflection
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190574
And from the earlier jacket retroreflective patch
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-19#post-190623
Some later measurements were claimed to be from a "direct hit" in a camera on the boat, however these "direct hits" lasted for over a minute while the boat moved significant distances perpendicular to the beam. This indicated a "direct hit" could be had anywhere within a large cone, meaning height estimates were possibly catching the bottom of the cone.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-18#post-190419
It was suggested geoid variations might be a factor, but did not seem to be significant
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-14#post-190169
Sandor claimed that a LIDAR study of the lake found it was flat, and that he had got confirmation of this. The lead author of the study refuted this.
https://www.metabunk.org/lake-balat...of-the-earth-if-any.t7780/page-23#post-190877
Sandor started a thread on scienceforums.net, and his OP seemed to suggest he was part of the LIDAR study, when he was not.
http://www.scienceforums.net/topic/98386-laser-curvature-test-on-lake-balaton/
Sandor was banned for a cumulation of violations of the posting guidelines, ending with his blatant misrepresentation of this paper (which actually proved the lake surface was curved exactly as would be expected)
The following is the original post that started the discussion
----------------------------------------------------------------
Water is absolutely FLAT
earth surface is 2/3 of water, so how can earth be a globe?
We have 33 meters (over 100 feet) missing target hidden height in our upcoming experiemnt!
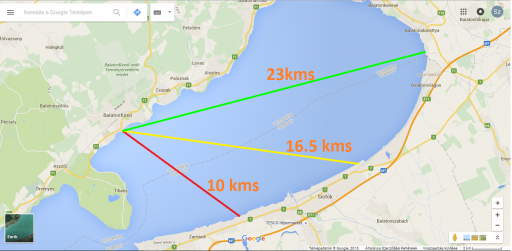
The 14.3 miles laser experiment will be in August 15th - 16th
Please visit us if you are nearby Hungary and lake Balaton!
Now we will have the 0.03 mRad collimator ready to keep laser beam divergence at 4 inch (10cms)diameter on the 14.3 miles (23kms) distance. With this exact pinpoint laser beam we can measure and calculate the refraction volume. We will measure ALL the distances in every 500 meters to get 30 to 50 points of measurement on each distance.
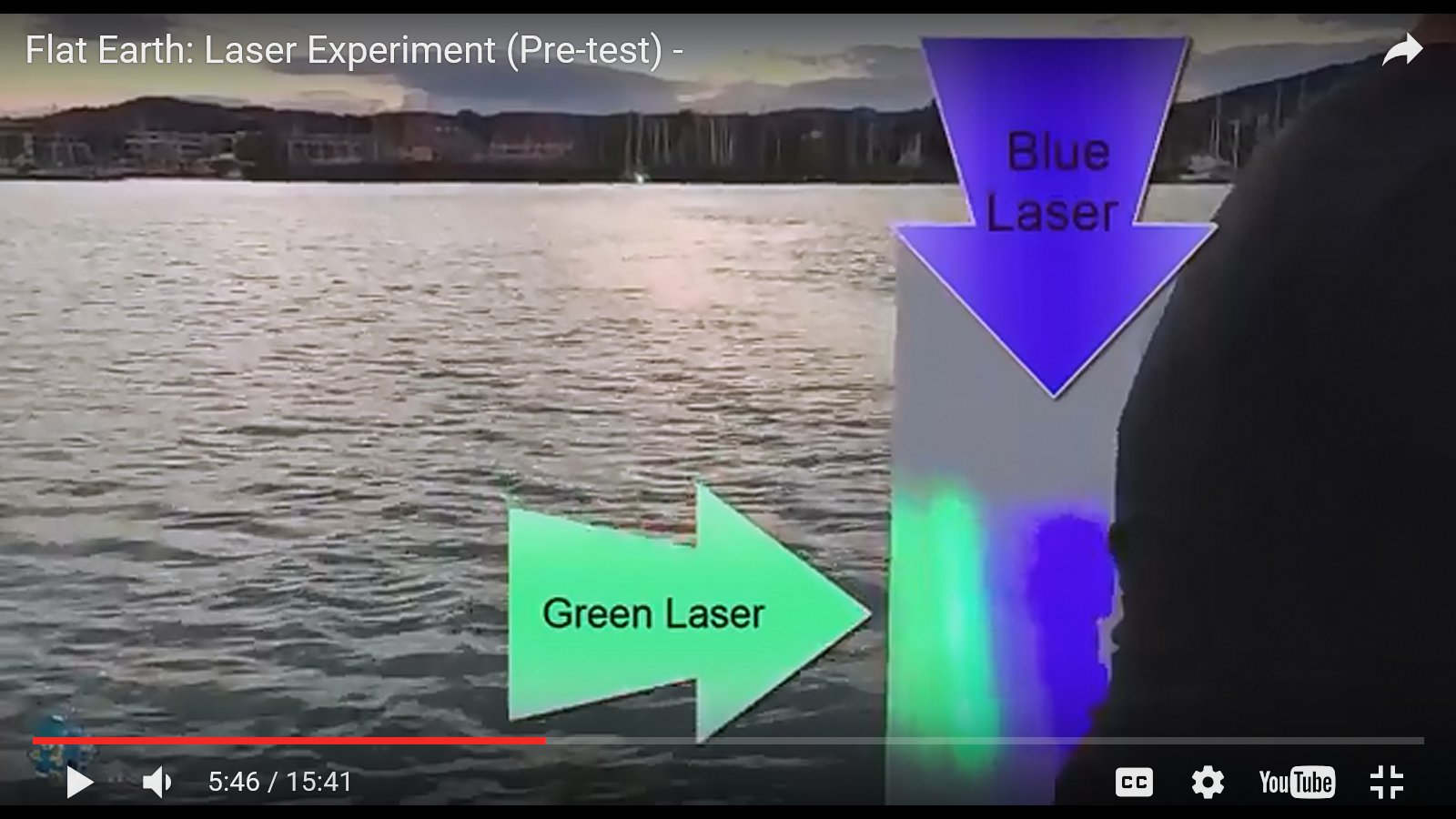
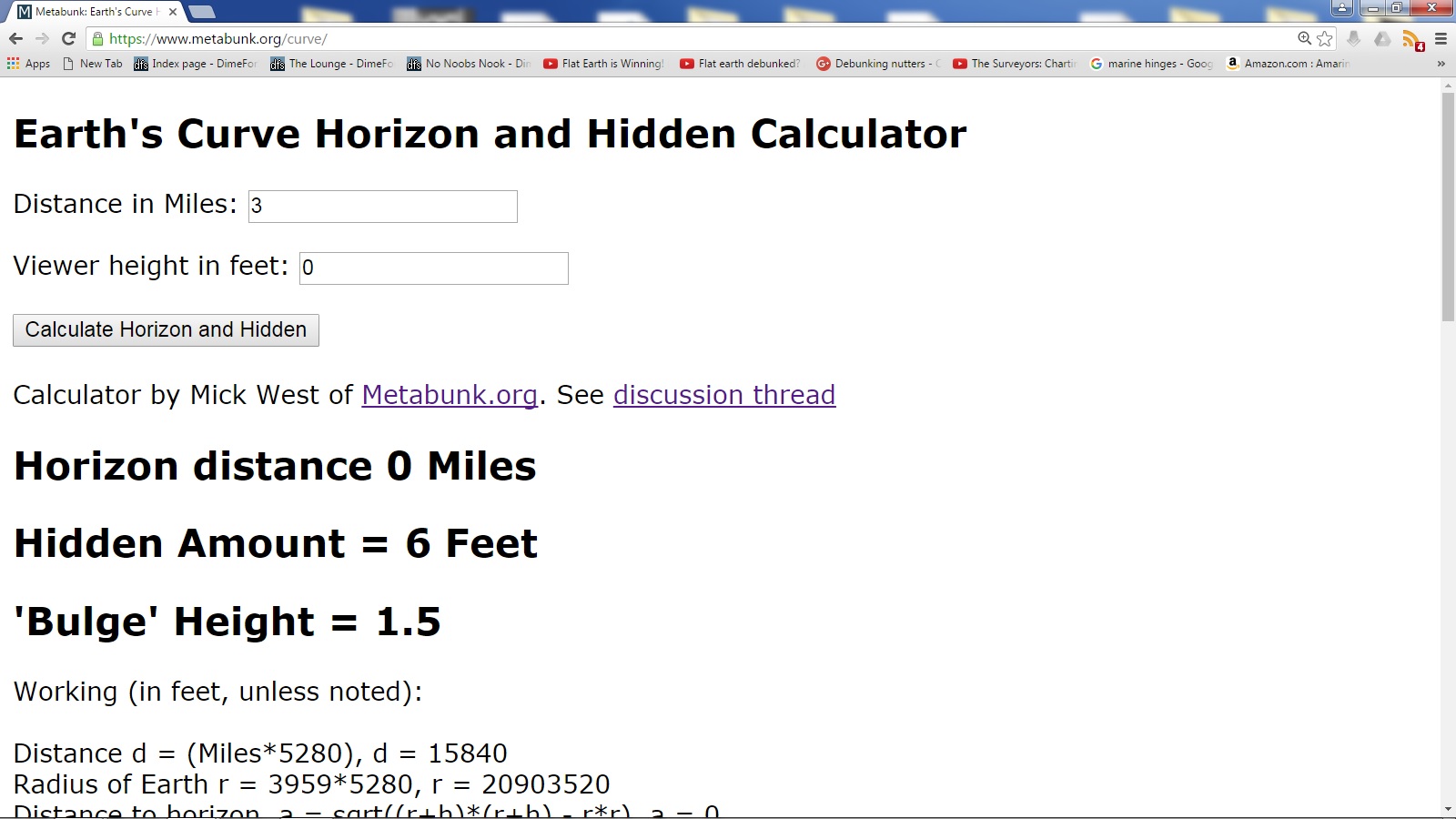
some pictures of our pre-test video that debunks Stephen Hoaxking's similar 3 miles curvature experiment with his ridiculous result of over 6 feet curvature drop on this distance, please watch here:
Source: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=cNEUOnlcIAQ
Attachments
Last edited by a moderator: